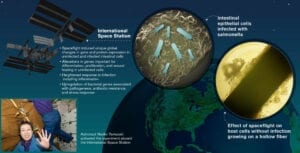
In the first study of its kind, Cheryl Nickerson, lead author Jennifer Barrila and their colleagues describe the infection of human cells by the intestinal pathogen Salmonella Typhimurium during spaceflight, Harth writes.
They show how the microgravity environment of spaceflight changes the molecular profile of human intestinal cells and how these patterns are further changed in response to infection. In another first, the researchers were also able to detect changes in the bacterial pathogen while inside the infected host cells, the scientist writes.
In the study, human intestinal epithelial cells were cultured aboard Space Shuttle mission STS-131, where a subset of the cultures were either infected with Salmonella or remained as uninfected controls.
“We appreciate the opportunity that NASA provided our team to study the entire infection process in spaceflight, which is providing new insight into the mechanobiology of infectious disease that can be used to protect astronaut health and mitigate infectious disease risks,” Harth quotes Nickerson. “This becomes increasingly important as we transition to longer human exploration missions that are further away from our planet.”
 SpaceWatch.Global An independent perspective on space
SpaceWatch.Global An independent perspective on space




