London, 13 December 2023.- Researchers are using a human-machine collaborative approach to assess areas of poverty in underdeveloped nations. Providing an accurate assessment of poverty is a global challenge with 53 countries not conducting agricultural surveys in the past 15 years, and 17 countries not publishing a population census. To fill the data gap new technologies are being explored to estimate poverty using street views, aerial photos, and satellite images.
A new paper titled “A human-machine collaborative approach measures economic development using satellite imagery” published in Nature Communications demonstrates how artificial intelligence (AI) can help analyse economic conditions from satellite imagery.
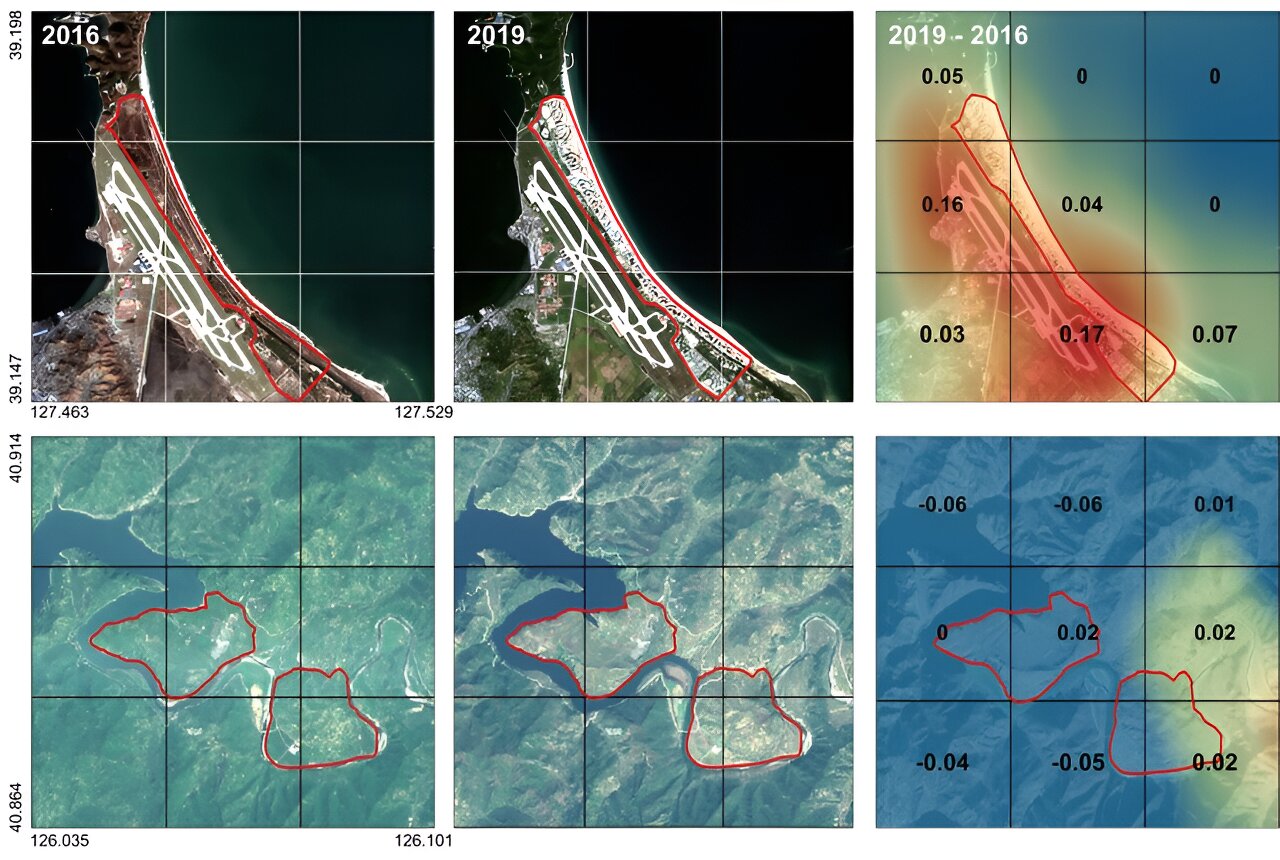
The researchers used Sentinel-2 satellite images from the European Space Agency (ESA). They were able to split the images into six-square-kilometre grids where the visual information can be used to quantify economic indicators. Using this technique the team produced an economic map of regions including North Korea, Nepal, Laos, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Cambodia.
The research was led by an interdisciplinary team of computer scientists, economists, and a geographer from KAIST & IBS (Donghyun Ahn, Meeyoung Cha, Jihee Kim), Sogang University (Hyunjoo Yang), HKUST (Sangyoon Park), and NUS (Jeasurk Yang).
“This is an important interdisciplinary effort to address global challenges like poverty,” said Meeyoung Cha, a data scientist on the team. “We plan to apply our AI algorithm to other international issues, such as monitoring carbon emissions, disaster damage detection, and the impact of climate change.”
This model could be used to rapidly monitor progress of Sustainable Development Goals such as reducing poverty and promoting more equitable and sustainable growth on an international scale. It could also be adapted to measure various social and environmental indicators such as identifying regions with high vulnerability to climate change and disasters to provide timely guidance.





