Edinburgh, 12 September 2022. – The ESA-NASA Solar Orbiter observatory found clues on the origin of magnetic structures dubbed switchbacks, and also revealed insights regarding the mechanisms that are likely to accelerate solar wind, the Metis Collaboration said.
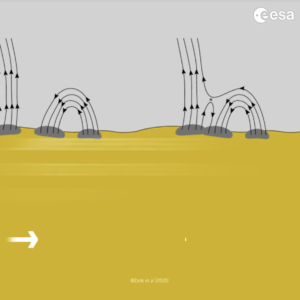
Solar Orbiter’s Metis coronagraph observed an S-shaped magnetic structure in the solar corona, propagating towards interplanetary space. The observations helped an international group of scientists to understand that switchbacks originate in the Sun’s corona.
Prof. Catia Grimani (Urbino University Carlo Bo) coordinates the topical team on cosmic rays within the Metis Collaboration. Working closely with her, Dr. Daniele Telloni, Metis Italian team member of the National Institute for Astrophysics, identified a structure similar to a switchback. The structure’s characteristics were similar to what was predicted by the mathematical model for the interchange reconnection theory.
Understanding the origins of such switchbacks may also answer questions about of the source of solar wind acceleration. Solar wind is coronal plasma moving radially away from the Sun interacting with Earth’s magnetosphere and infrastructure.
The results were presented at the 8th Solar Orbiter Workshop in Belfast, Northern Ireland and published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.





